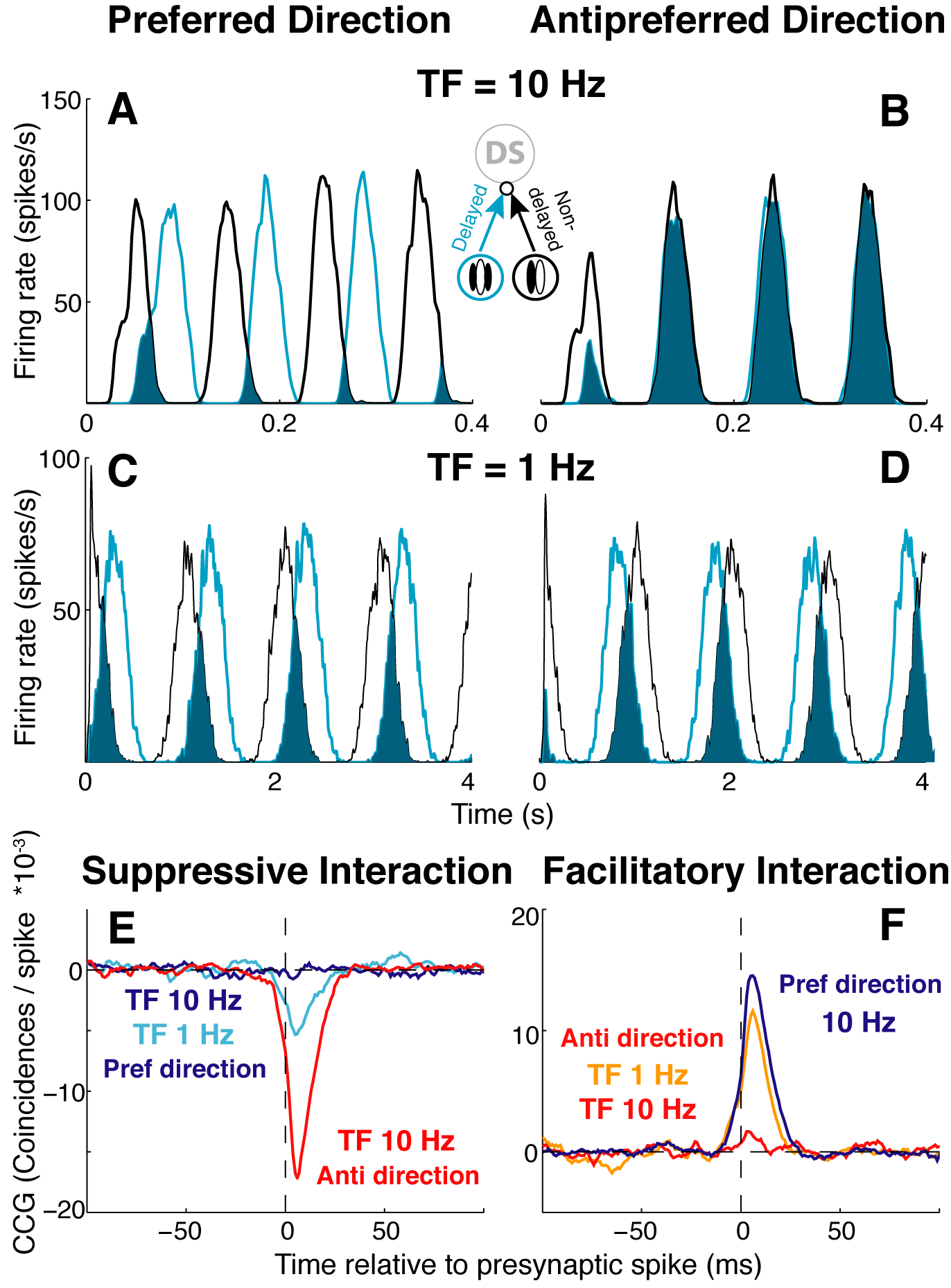
The stimulus dependence of CCG features in the reflects changes in relative timing of input spikes as stimulus parameters are varied.
(A) PSTHs from TF 10 Hz, preferred direction motion for 2 EX units that form a DS subunit in the suppressive Presynaptic Delay model.
(B) PSTHs from TF 1 Hz, preferred direction motion for 2 EX units that form a DS subunit in the suppressive Presynaptic Delay model.
(C) PSTHs from TF 10 Hz, anti-preferred direction motion for 2 EX units that form a DS subunit in the suppressive Presynaptic Delay model.
(D) PSTHs from TF 1 Hz, anti-preferred direction motion for 2 EX units that form a DS subunit in the suppressive Presynaptic Delay model.
(E) CCGs in the suppressive Presynaptic Delay model as stimulus direction and temporal frequency are varied.
(F) CCGs in the facilitatory Presynaptic Delay model as stimulus direction and temporal frequency are varied.
(Supplemental Data) CCGs in the facilitatory and suppressive Postsynaptic Delay models as stimulus direction and temporal frequency are varied.